
Comparatively, the dB (decibel) is a used for quantifying rations between values such as noise to signal ratio, which makes it a dimensionless unit. The unit of measurement is used when measuring absolute power given that it is an absolute unit referenced to the watt. It is preferred since it can express both very small and very large values in short form as compared to the BW, whose smallest unit is 1000 mW – one watt.
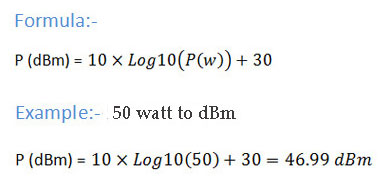
The reference finds application in fiber optical communication, microwave and radio networks to express absolute power. 120 dBm = 0.224 microvolts.ĭBm / dB(mW) is sometimes referred to as decibel milliwatts. There are times when spec sheets may show the voltage & power level e.g. When used in the 2-way radio field, the dB is referenced to a 50 ohm load, with the resultant voltage being 0.224 volts. When used in audio work the milliwatt is referenced to a 600 ohm load, with the resultant voltage being 0.775 volts. Countries will typically have specific regulations on how much power an antenna may emit. On the other hand, very high dBms can result in the amplification of interference and background noise, which will result in a poor quality signal. Low dBms provide weak connections and may make working with such a router difficult or even impossible. We measure that power in milliwatts which is typically abbreviated as mW.Īs such, if you have a WiFi router, dBm measures the power the antenna is emitting, which can play a significant role in how much range the router has. We use dBm when we are measuring power emitted from amplifiers. dbm is logarithmic and mw is linear.ĭBm dB (mW): dBm is is an expression of power in decibels per milliwatt.
A good illustration of this is when you are using an application such as a Wi-Fi router. Linear polarization of the EM field is assumed unless noted otherwise.ĭBi refers to decibels measured against an isotropic reference antenna.
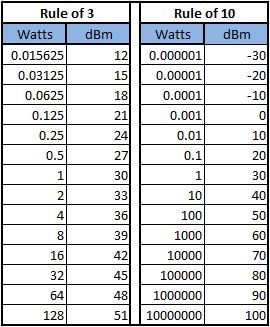
The forward gain is compared with the hypothetical isotropic antenna, which uniformly distributes energy in all directions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
